Cladding vs. Weld Overlay: What’s the Deal?
We often hear the terms “cladding” and “weld overlay” used synonymously – and while the two terms are related, they do differ.
We asked the engineering experts at McCrometer to weigh in on the similarities and differences between cladding and weld overlay, and here’s what you need to know!
The Basics of Cladding
Cladding is the broad term for applying one material over another to provide a coating or covering. When it’s regarding flow meters, it’s the process of applying a better metallic surface over another surface to improve the properties, usually corrosion-resistance. These metals are typically more expensive than their corrosive alternatives, so cladding is a cost-effective method of providing corrosion-resistance compared to the price of manufacturing a homogenous flow meter.
Pipes and flow meters can be clad through a variety of methods, the most popular being weld overlay, allowing the base material to be completely protected from corrosion or harsh chemicals by a metallic alloy welded onto the base material. Other popular methods include hard-facing, which utilizes a spray or explosion-bonding process to increase the hardness of a surface. This is especially helpful in applications experiencing sand or rock particulates in the flow which may damage certain metallic surfaces.
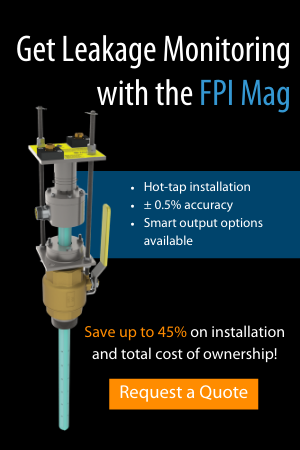
McCrometer’s V-Cone® product suite is highly customizable in both exotic material construction as well as cladding, allowing the V-Cone to fit a wide range of customer applications. The oil and gas industry, a popular market for the V-Cone, often has highly corrosive media flowing through pipes, such as crude oil and gasses like hydrogen sulfide.
Why Clad?
When deciding to clad, a few factors should be considered. If the flow project calls for a small line size V-Cone, the material cost savings won’t be significant if you choose to clad. Choosing a homogenous exotic material to manufacture the V-Cone may be similar in price, and depending on the material requirements it may also lessen the lead time for manufacturing.
However, just as the price of the meter increases when the line size increases, so do material costs. McCrometer customers operating in the oil and gas industry often choose to have their large line size V-Cones made of carbon-steel and cladded with a nickel alloy, Inconel, or even stainless steel.
These more expensive materials ensure the longevity of the meter and the pipeline as a whole, as high-quality corrosion-resistant metals can withstand the harsh conditions of numerous oil and gas applications. The V-Cone is an investment meter that requires minimal-to-no maintenance and offers up to ±0.5% accuracy throughout its proven 25+ year lifespan. Ensuring that corrosion doesn’t diminish the V-Cone’s value and continual benefits is required to maintain optimal production in your flow application.
Protecting Your Flow Meter Investment
While protecting the meter from the process fluid is typically the main reason for cladding, there’s also the outside environment to consider as well. If the meter’s interior has been cladded but the exterior is still the base material, corrosion from seawater, extreme temperatures, abrasion from desert sand, or other environmental factors may affect the integrity of the meter’s construction.
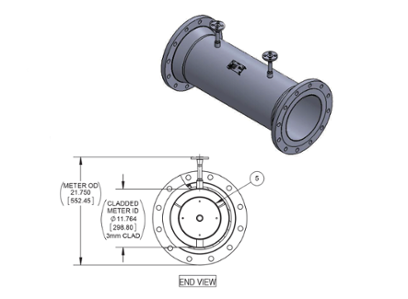
A general arrangement drawing for a V-Cone cladded with Inconel.
McCrometer’s engineering experts also recommend fabricating the meter’s pressure taps from the same material as the cladding; protecting your meter and piping is important but neglecting a critical point such as the pressure taps leaves your meter vulnerable to that corrosion. McCrometer can clad with a variety of materials such as duplex stainless steel, Inconel, nickel alloys, and other materials from the nickel and steel families. Inconel happens to be a popular choice with our oil and gas customers as it resists just about every corrosive fluid and media.
Customers in industrial markets will often decide to clad their meter if they are flowing a media with corrosive fluids or debris particulates. Even some operations managers flowing steam or super-heated steam may opt for a cladded meter so they don’t need to worry about the minimal carbon steel corrosion that’s likely to happen in that application.
Deciding to Clad Your Meter
While some customers have precise engineering specifications that denote cladding, other customers may need to weigh their options to decide what will allow them to achieve their project goals. We recommend reaching out to the McCrometer factory to speak to our experts; having a discussion with our engineers can provide you with valuable information on our processes, available options, and factors like cost and turnaround time.
As a customer considering cladding, the best thing you can do is provide the McCrometer factory with as much information about your application and flow project as possible so our team can prescribe a solution that will provide you with the most longevity and value for your investment.
For more information, contact the factory.
Cladding vs. Weld Overlay: What’s the Deal?
Related Posts
Featured Posts
Choosing the Right Non-Contact Flow Meters: A Quick Dive into Radar and Laser Technologies
When measuring open channel flow wastewater and stormwater, non-contact flow technology is the ideal method, able to provide an accurate velocity and flow rate. Especially in the wet weather season, non-contact flow technology greatly benefits open channel...
Meeting BABA Compliance And Expanding Opportunities
Content Recorded and Published at WEFTEC in October 2024 In this episode of The Water Online Show: On Location, (now former) McCrometer President Pete Oveson dives into the company's story and recent developments shaping its future. He begins with an overview of...
McCrometer, Inc. Announces Redesign of FlowComTM Digital Register
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: September 3rd, 2024Contact: Aimee Davis, Vertical Marketing Manager, Agriculture McCrometer, Inc.AimeeD@mccrometer.com Hemet, Calif. – McCrometer, Inc., a globally recognized flow meter manufacturer, today announced the launch of their...
Request More Information